Learning Outcomes
i. Define dehydration-synthesis and hydrolysis reactions.
ii. Explain the importance of dehydration-synthesis and hydrolysis reactions to life.
iii. Identify the different types of macromolecules that are formed by dehydration-synthesis reactions and the different types of macromolecules that are broken down by hydrolysis reactions.
i. Dehydration-synthesis reactions:
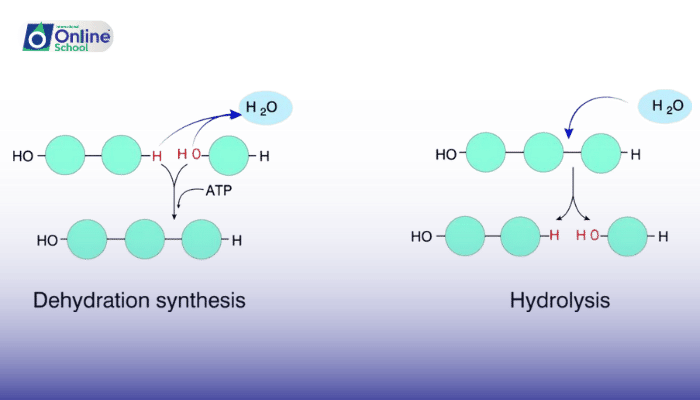
Dehydration-synthesis reactions are chemical reactions that build macromolecules by removing water molecules. Macromolecules are large molecules that are made up of many smaller molecules, called monomers. Dehydration-synthesis reactions are also called condensation reactions.
To build a macromolecule, two monomers must come together and remove a water molecule. This is done by forming a covalent bond between the two monomers. The process of removing a water molecule is called dehydration.
The following is an example of a dehydration-synthesis reaction:
Glucose + Glucose -> Maltose + Water
In this reaction, two glucose molecules come together and remove a water molecule to form a maltose molecule. Maltose is a disaccharide, which is a type of carbohydrate that is made up of two monosaccharides.
Dehydration-synthesis reactions are important for life because they are used to build all of the macromolecules that are essential for life, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids.
ii. Hydrolysis reactions
Hydrolysis reactions are chemical reactions that break down macromolecules by adding water molecules. Hydrolysis reactions are the opposite of dehydration-synthesis reactions.
To break down a macromolecule, a water molecule is added to the macromolecule. This breaks the covalent bond between two monomers. The process of adding a water molecule is called hydration.
The following is an example of a hydrolysis reaction:
Maltose + Water -> Glucose + Glucose
In this reaction, a water molecule is added to a maltose molecule to break it down into two glucose molecules.
Hydrolysis reactions are important for life because they are used to break down macromolecules into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy or to build new molecules.
Types of macromolecules formed by dehydration-synthesis reactions
i. Carbohydrates
ii. Proteins
iii. Lipids
Types of macromolecules broken down by hydrolysis reactions
i. Carbohydrates
ii. Proteins
iii. Lipids
Relationship between dehydration-synthesis and hydrolysis reactions
Dehydration-synthesis reactions and hydrolysis reactions are opposite reactions. Dehydration-synthesis reactions are used to build macromolecules by removing water molecules, while hydrolysis reactions are used to break down macromolecules by adding water molecules.
Real-world applications of dehydration-synthesis and hydrolysis reactions
Dehydration-synthesis and hydrolysis reactions are used in a variety of products and industries. For example, dehydration-synthesis reactions are used to produce food products, such as bread and pasta. Hydrolysis reactions are used to produce biofuels, such as ethanol, and to break down plastics.
Dehydration-synthesis and hydrolysis reactions are essential for life. Dehydration-synthesis reactions are used to build all of the macromolecules that are essential for life, while hydrolysis reactions are used to break down macromolecules into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy or to build new molecules.